Trekking is not just a walk in the woods; it's an exhilarating journey that demands varying levels of skill, endurance, and preparation. Whether you're a seasoned trekker or a novice adventurer, understanding trekking grades can significantly enhance your experience and ensure you choose the right expedition for your abilities and interests.
What is Trekking Grade Classification?
Trekking grade classification categorizes trekking routes based on their difficulty level, taking into account factors such as altitude, terrain, duration, and technical challenges. This classification system helps trekkers assess the demands and risks associated with each trek, allowing them to make informed decisions and adequately prepare for their adventure.
Classification of Trekking Grade
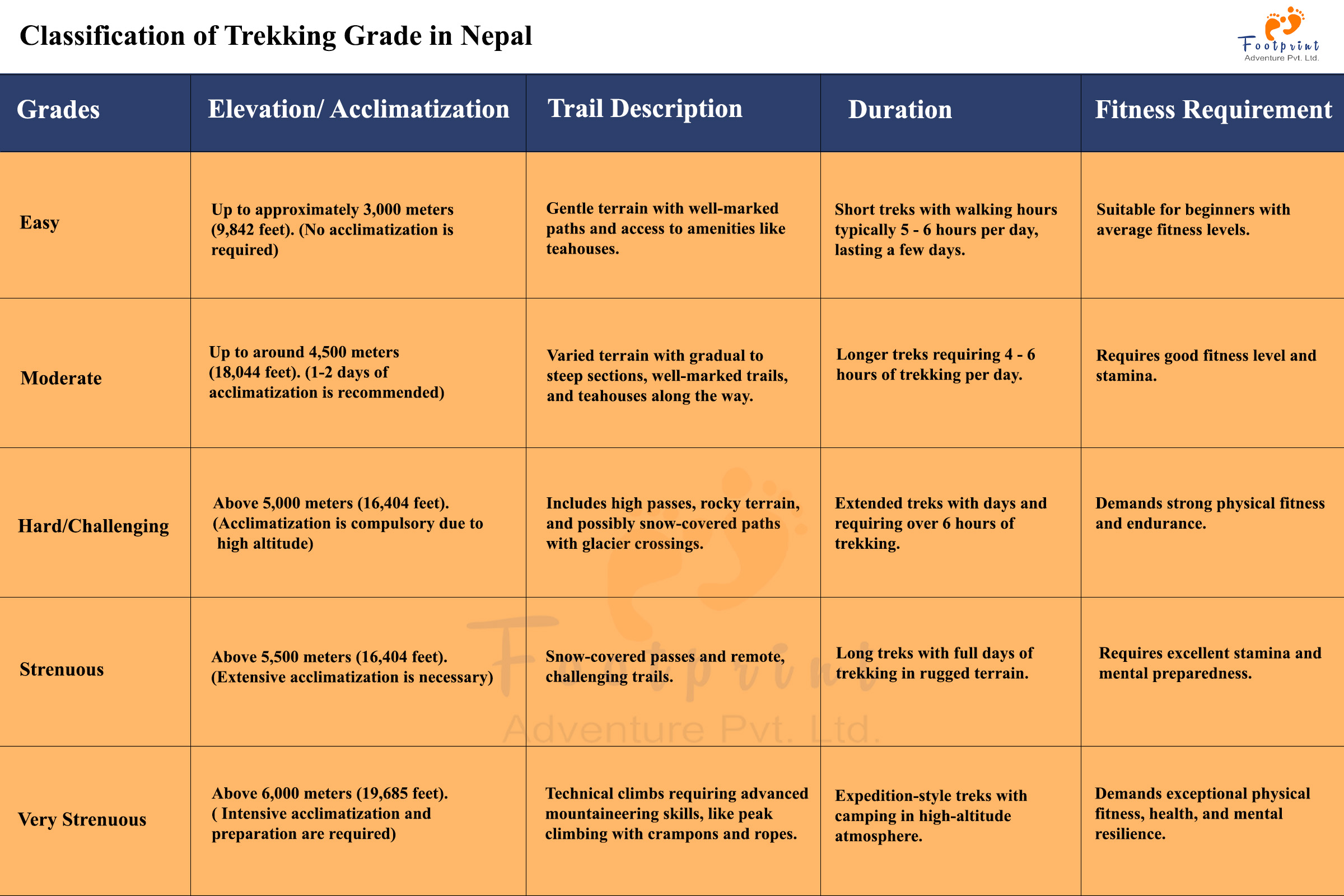
1. Easy:
- Elevation: Up to approximately 3,000 meters (9,842 feet).
- Trail Description: Gentle terrain with well-marked paths and access to amenities like teahouses.
- Duration: Short treks with walking hours typically 5 to 6 hours per day, lasting a few days.
- Fitness Requirement: Suitable for beginners with average fitness levels.
- Acclimatization: No acclimatization is required.
- Examples: Shivapuri Nagarkot Hike, Khumai Danda Trek, etc.
2. Moderate:
- Elevation: Up to around 5,000 meters (18,044 feet).
- Trail Description: Varied terr,ain with gradual to steep sections, well-marked trails, and teahouses along the way.
- Duration: Longer treks requiring 4-6 hours of trekking per day.
- Fitness Requirement: Requires good fitness and stamina.
- Acclimatization: 1-2 days of acclimatization is recommended.
- Examples:Langtang Valley Trek, Helambu Trek, Manaslu Circuit Trek, etc.
3. Hard/Challenging:
- Elevation: Above 5,000 meters (16,404 feet).
- Trail Description: Includes high passes, rocky terrain, and possibly snow-covered paths with glacier crossings.
- Duration: Extended treks with days requiring over 6 hours of trekking.
- Fitness Requirement: Demands strong physical fitness and endurance.
- Acclimatization: Essential due to high altitudes.
- Examples:Annapurna Circuit Trek,Upper Dolpo Trek,Nar Phu Valley Trek, etc.
4. Strenuous:
- Elevation: Above 5,500 meters (16,404 feet).
- Trail Description: Snow-covered passes and remote, challenging trails.
- Duration: Long treks with full days of trekking in rugged terrain.
- Fitness Requirement: Requires excellent stamina and mental preparedness.
- Acclimatization: Extensive acclimatization is necessary.
- Examples:Everest Base Camp Trek via Gokyo Lakes, Kanchenjunga Circuit Trek, Rolwaling Valley Trek, etc.
5. Very Strenuous:
- Elevation: Above 6,000 meters (19,685 feet).
- Trail Description: Technical climbs requiring advanced mountaineering skills, including peak climbing with crampons and ropes.
- Duration: Expedition-style treks with camping in high-altitude environments.
- Fitness Requirement: Demands exceptional physical fitness, health, and mental resilience.
- Acclimatization: Intensive acclimatization and preparation are required.
- Examples:Everest Three Passes Trek, Makalu Base Camp, Barun Valley Trek, Ama Dablam Expedition, Island Peak Climbing with EBC Trek, etc
Conclusion
Understanding the trekking grade classifications in Nepal helps trekkers choose a route that aligns with their skills, fitness level, and readiness for high-altitude conditions. Whether you're seeking a leisurely hike or a challenging summit climb, these classifications ensure a safe and rewarding trekking experience amidst Nepal's breathtaking landscapes.

